Protect Your Smile: Understanding Gum Disease and How to Treat and Prevent It!
Gum Diseases: Types, Treatment, and Prevention Methods
Gum diseases are serious issues that can threaten oral health and, if left untreated, lead to tooth loss. In this article, you will find detailed information about the types of gum diseases, treatment methods, and ways to prevent these diseases. Additionally, we will address the causes of gum disease and answer frequently asked questions.
1. What Are Gum Diseases?
Gum diseases are typically defined as inflammations affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. Here are the most common types of gum diseases:
1.1 Gingivitis:
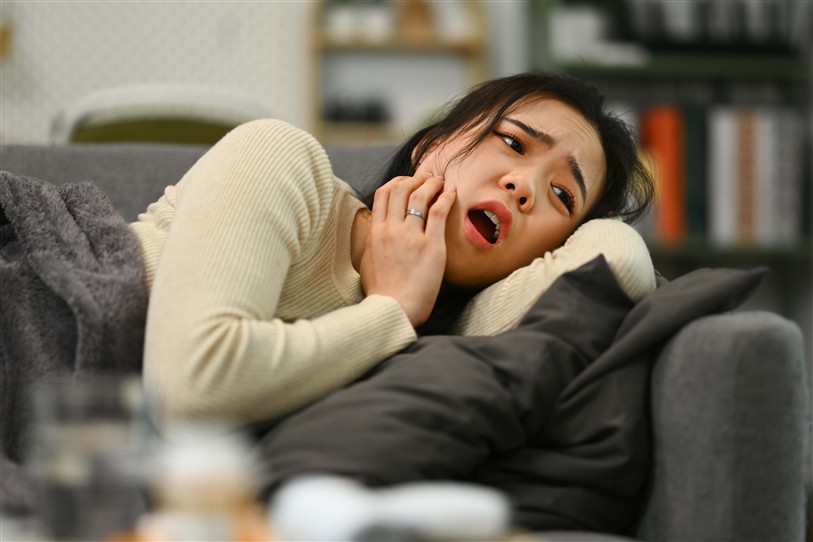
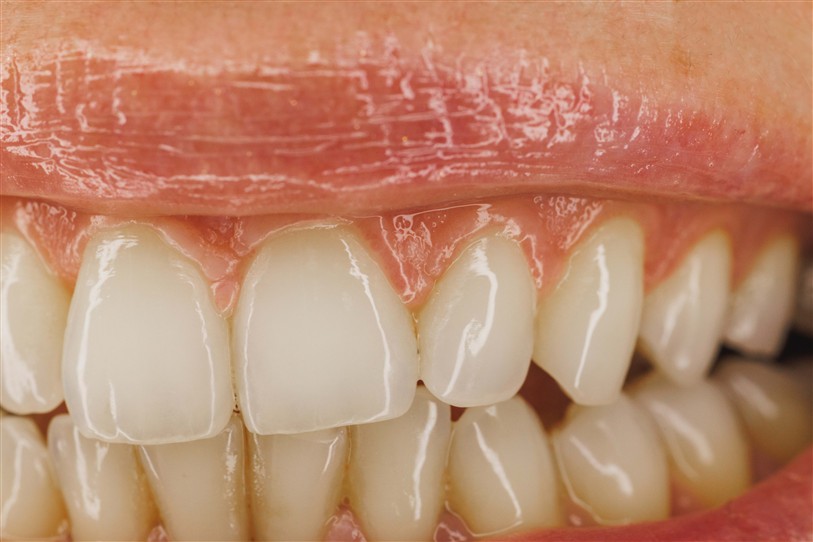
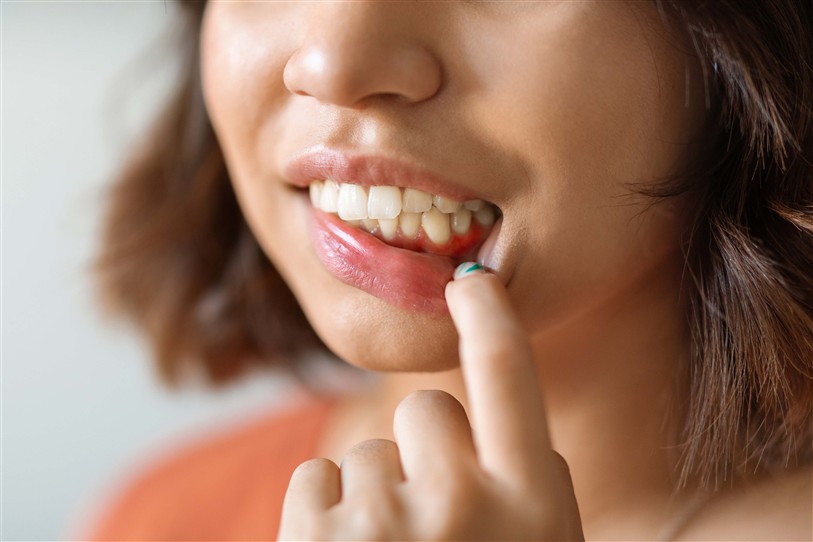
- Definition: The mildest form of gum disease. It manifests as inflammation of the gums and is usually painless.
- Symptoms: Redness, swelling, and bleeding during brushing.
- Treatment: It is fully reversible with good oral hygiene and regular dental cleanings.
1.2 Periodontitis:
- Definition: Occurs when untreated gingivitis progresses. The gums recede, and the bones supporting the teeth are damaged.
- Symptoms: Gum recession, loose teeth, bad breath.
- Treatment: Deep cleaning (scaling), antibiotics, and in advanced cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.
1.3 Aggressive Periodontitis:
- Definition: A rapidly progressing gum disease that occurs in young individuals. Genetic factors play a role.
- Treatment: Advanced treatment methods and frequent dental check-ups are required.
1.4 Chronic Periodontitis:
- Definition: Leads to the gradual loss of the supporting tissues of the teeth. It is common in middle-aged and older individuals.
- Treatment: Regular dental cleanings, root planing, and sometimes surgical intervention.
2. Causes of Gum Diseases
The most common cause of gum diseases is plaque buildup on the teeth. Plaque is a sticky film full of bacteria that forms on the surface of the teeth. If plaque is not regularly removed, it hardens and turns into tartar, which irritates the gums and leads to inflammation. Here are other factors that can contribute to gum disease:
- Poor oral hygiene: Without regular brushing and flossing, plaque accumulation increases rapidly.
- Genetic factors: Individuals with a family history of gum disease are at higher risk.
- Smoking and tobacco use: Smoking is one of the biggest risk factors for gum disease.
- Stress: The body’s resistance to infections decreases when under stress, paving the way for gum diseases.
- Poor nutrition: Vitamin deficiencies, especially a lack of vitamin C, can negatively affect gum health.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, puberty, and menopause can make the gums more sensitive.
3. How Are Gum Diseases Treated?
The treatment of gum disease varies depending on the type and severity of the disease. Here are the treatment methods:
- Regular Dental Cleanings: Early-stage gum diseases like gingivitis can be treated with regular dental cleanings and good oral hygiene.
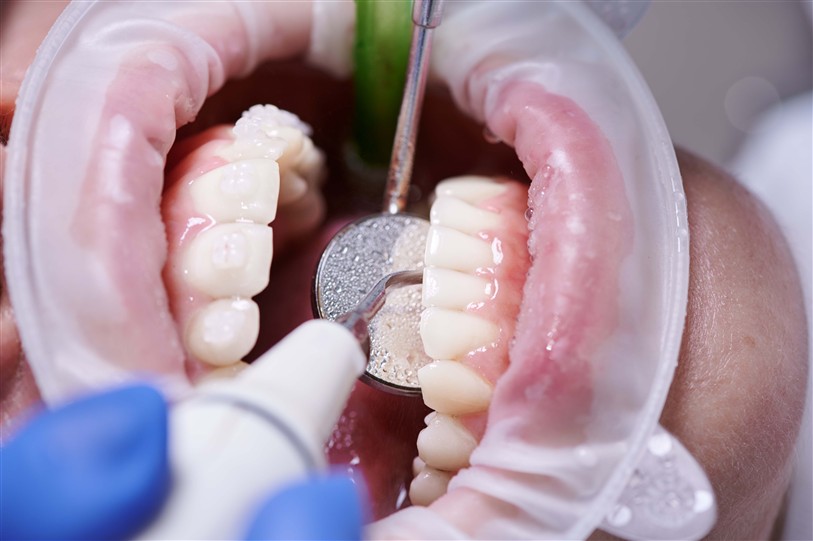
- Scaling and Root Planing: In cases of periodontitis, deep cleaning is performed to remove plaque and tartar beneath the gums. Additionally, rough surfaces on the roots are smoothed to make it harder for bacteria to adhere.
- Antibiotic Treatment: Oral or topical antibiotics may be used to control inflammation.
- Surgical Intervention: In advanced cases, surgical treatment may be necessary to repair the tissues damaged in the gums and bones.
4. How Can Gum Diseases Be Prevented?
Preventing gum disease is possible with a simple but effective oral care routine. Here are the most effective prevention methods:
- Regular Brushing and Flossing: Brushing your teeth at least twice a day and using dental floss daily helps prevent plaque buildup.
- Dental Check-Ups: Regular visits to the dentist allow for the early diagnosis of gum diseases.
- Balanced Diet: Consuming adequate vitamins and minerals helps maintain gum health.
- Avoiding Smoking and Tobacco Products: Quitting smoking significantly reduces the risk of gum disease.

5. Frequently Asked Questions
5.1 What happens if gum diseases are not treated?
Untreated gum diseases can lead to tooth loss, damage to the jawbone, and serious oral infections.
5.2 Are gum diseases painful?
Gingivitis is typically painless, but advanced stages like periodontitis can cause pain and discomfort.
5.3 How can gum recession be prevented?
Preventing gum recession requires good oral hygiene practices, regular dental visits, and a diet that supports gum health.
5.4 Are gum diseases contagious?
Gum diseases are caused by bacteria but are not directly contagious. However, individuals in the same environment may share similar risk factors.
5.5 Can pregnancy trigger gum diseases?
Yes, hormonal changes during pregnancy can make the gums more sensitive and prone to inflammation.
6. Conclusion
Gum diseases are preventable and treatable health issues. Regular dental cleanings, the use of dental floss, and visits to the dentist are the most effective ways to maintain gum health. If you notice swelling, bleeding, or receding gums, don’t hesitate to contact your dentist.
If you have any questions or would like more information about your dental health, feel free to reach out to our clinic!










Do Comment